Predictive maintenance for corrugated machinery is becoming essential in modern box plants. Corrugated production lines are built to run fast and run long — until something breaks. Unplanned downtime caused by tool failure, misalignment, or overheating can cripple productivity. For tips on tackling these common issues, read our troubleshooting guide.
That’s why leading plants are shifting from reactive fixes to predictive maintenance: a proactive strategy that uses sensors, data, and smart scheduling to detect failures before they happen. Learn more about how predictive maintenance works in manufacturing from this industry guide.
Predictive maintenance (PdM) uses real-time data from machines to anticipate component wear or failure. Unlike preventive maintenance, which follows a fixed schedule, PdM monitors the actual condition of parts like slotting knives, corrugating rolls, motors, and bearings — so you act only when needed.
Predictive maintenance can seem like an investment upfront. However, the savings in downtime, labor, and replacement parts often pay for themselves within the first year.
- Less downtime: Stop breakdowns before they stop production — AI‑enabled analytics can identify problems before they arise source.
- Smarter parts replacement: Replace only when performance drops — not just by the calendar.
- Longer component life: Optimize regrind and sharpening cycles for tooling like scoring rings.
- Vibration: Spikes may signal bearing wear or motor imbalance.
- Temperature: Unusual heat may point to friction, failed lubrication, or misalignment.
- Cycle counts: Track exact usage of wear parts like tab knives and slotting heads.
- Moisture levels: For corrugator steam and paper control systems.
- Identify a critical machine or part — start small with high‑impact assets (for example, corrugating rolls; see our corrugating roll maintenance guide).
- Install basic sensors — temperature, vibration, or amp draw meters are affordable and effective.
- Log and review data monthly to spot trends.
- Create alerts for anomalies — before failure occurs.
For example, say your scoring ring pressure gradually increases—indicating wear.
A vibration sensor alerts the team.
Instead of waiting for a blowout or failed box batch, you schedule a swap at shift change.
As a result, there’s no overtime. No scrap. No lost orders.
Predictive maintenance only works when parts are ready. Corrugated Replacements stocks exact-fit scoring rings, knives, and holders — plus we can help you create a replacement schedule tailored to your machine’s wear patterns. Need help sourcing sensor kits or aligning with a PdM dashboard? Ask our technical team for guidance.
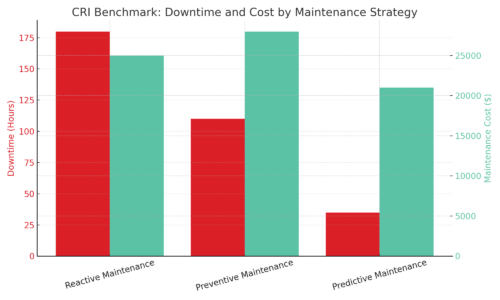
Choosing the right maintenance strategy isn’t just about cost — it’s about keeping your line moving. The table below compares average annual downtime and maintenance costs across three common approaches: reactive, preventive, and predictive maintenance. The numbers speak for themselves.
| Strategy | Downtime (hrs/year) |
Maintenance Cost (USD/year) |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reactive Maintenance | 180 | $25,000 | Run-to-failure; high risk of unexpected shutdowns |
| Preventive Maintenance | 110 | $28,000 | Fixed intervals; some over-servicing |
| Predictive Maintenance | 35 | $21,000 | Sensor-based; addresses problems before failure |
In short, predictive maintenance isn’t just a future trend — it’s what smart plants are doing today to cut costs and avoid last-minute chaos.
Therefore, if you haven’t already started monitoring machine health, now is the time.
With the right tools and strategy, you can prevent breakdowns before they start.